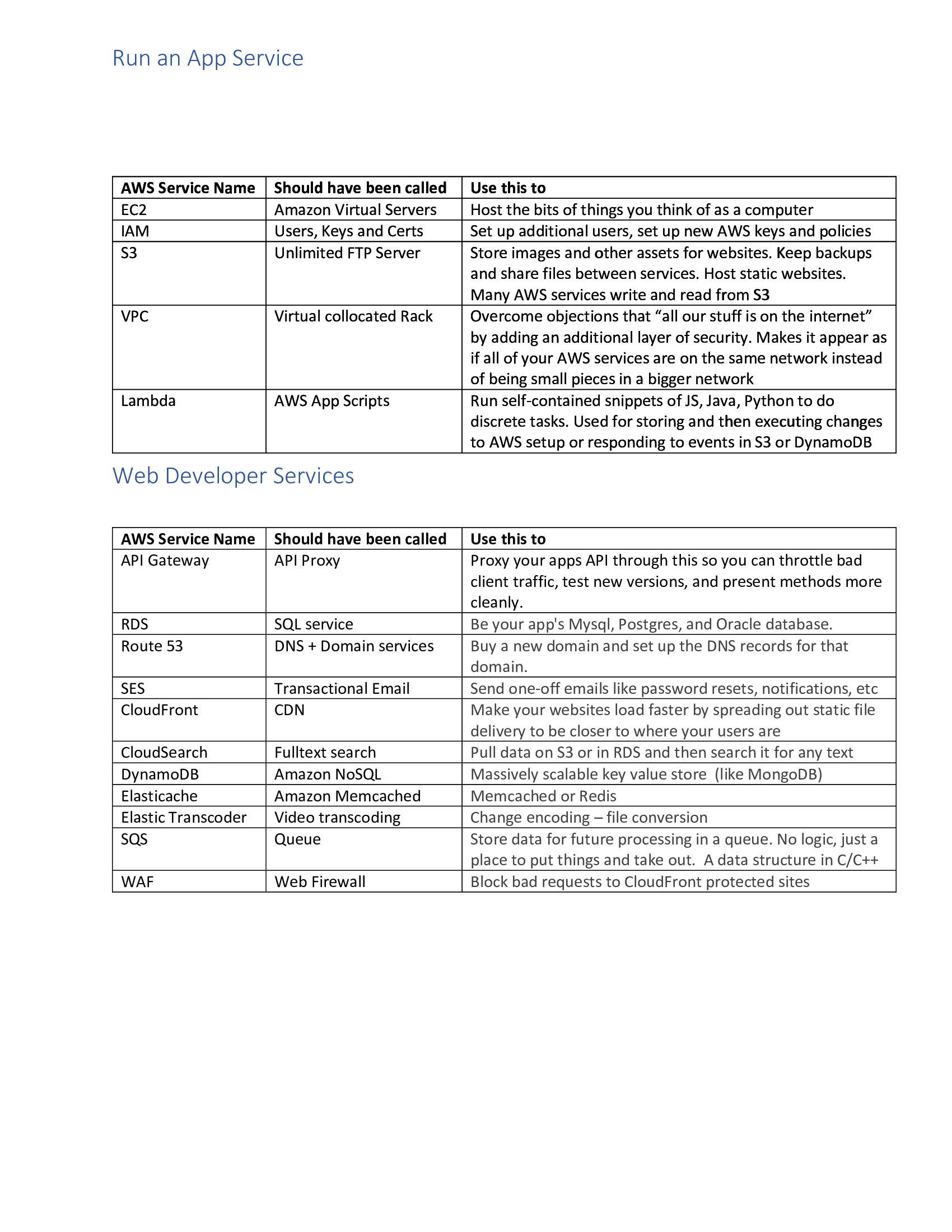
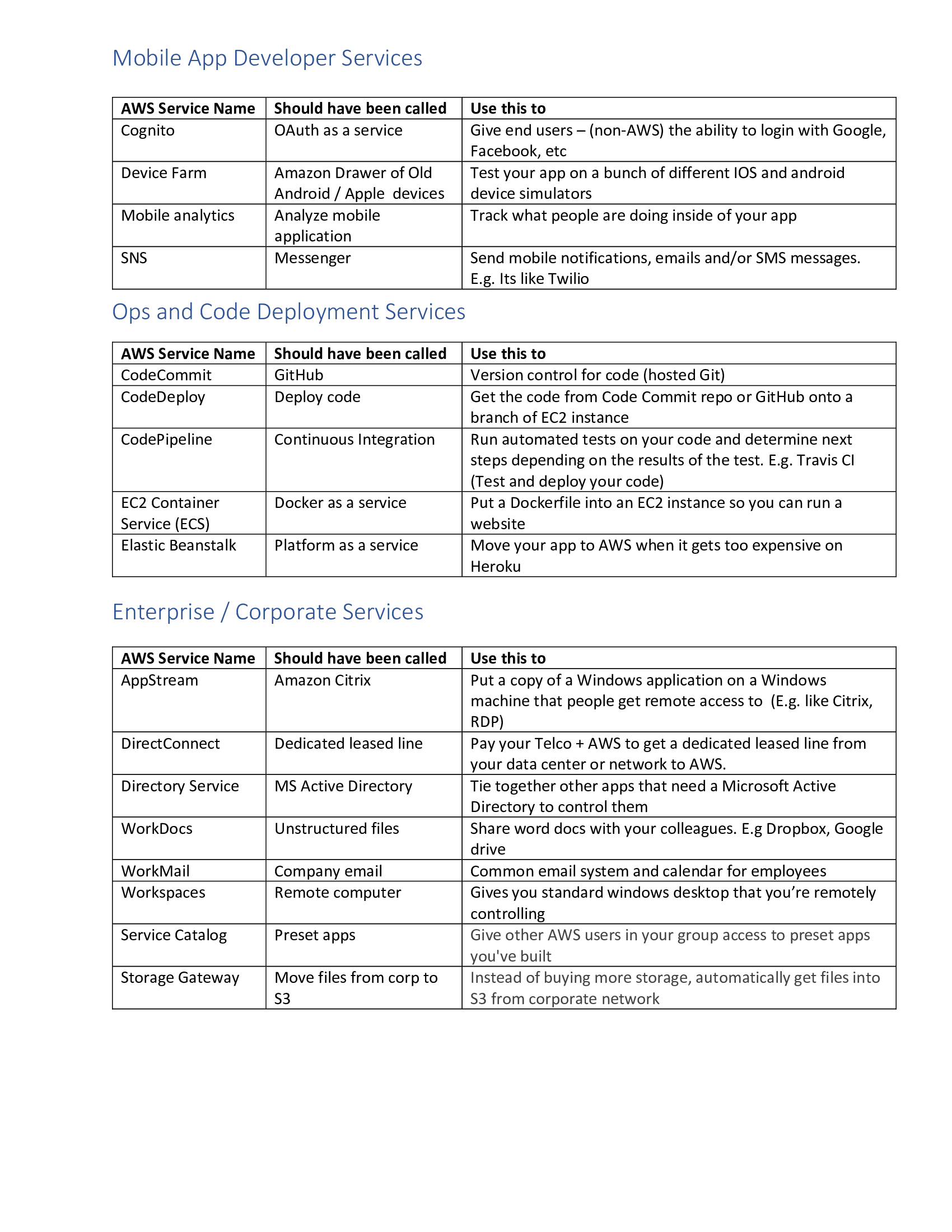
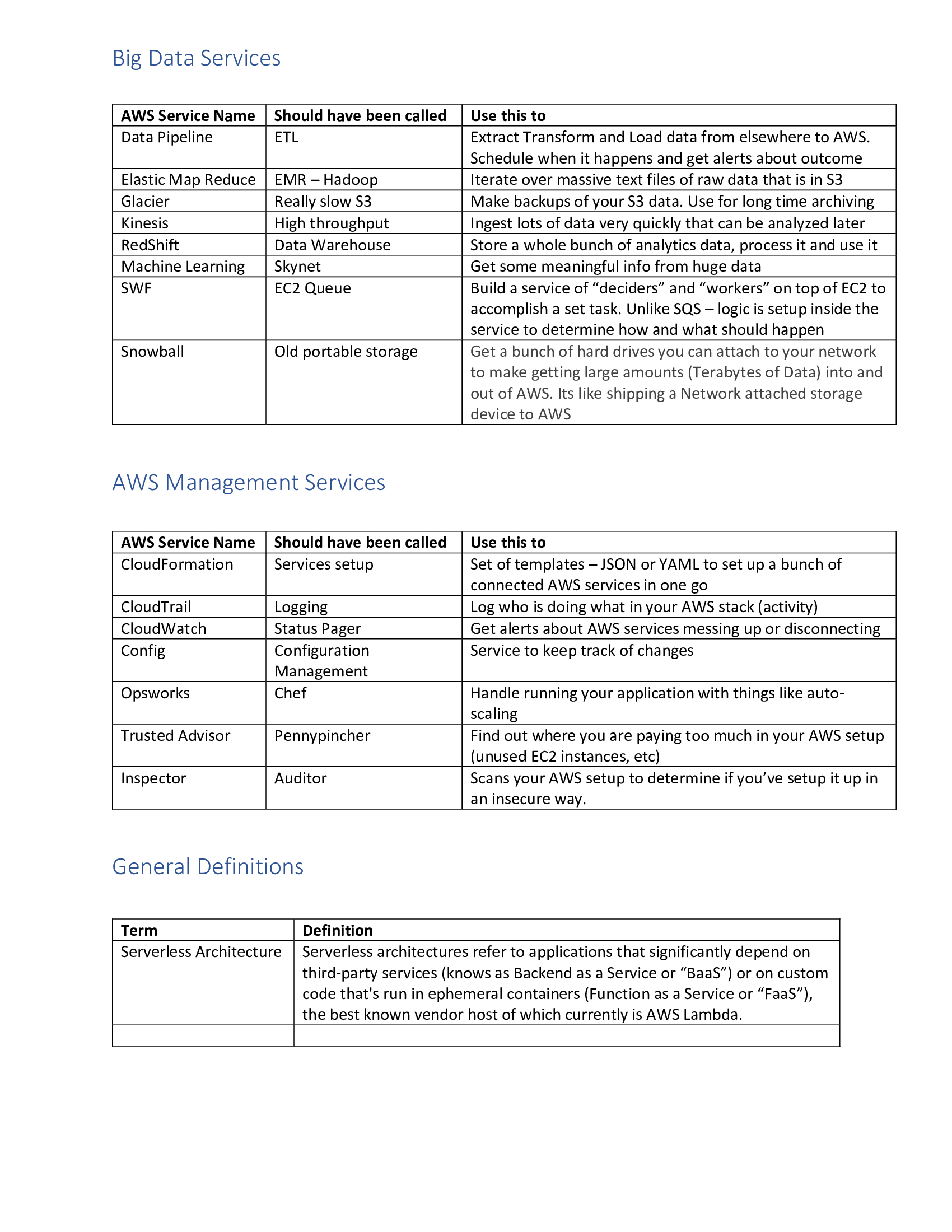
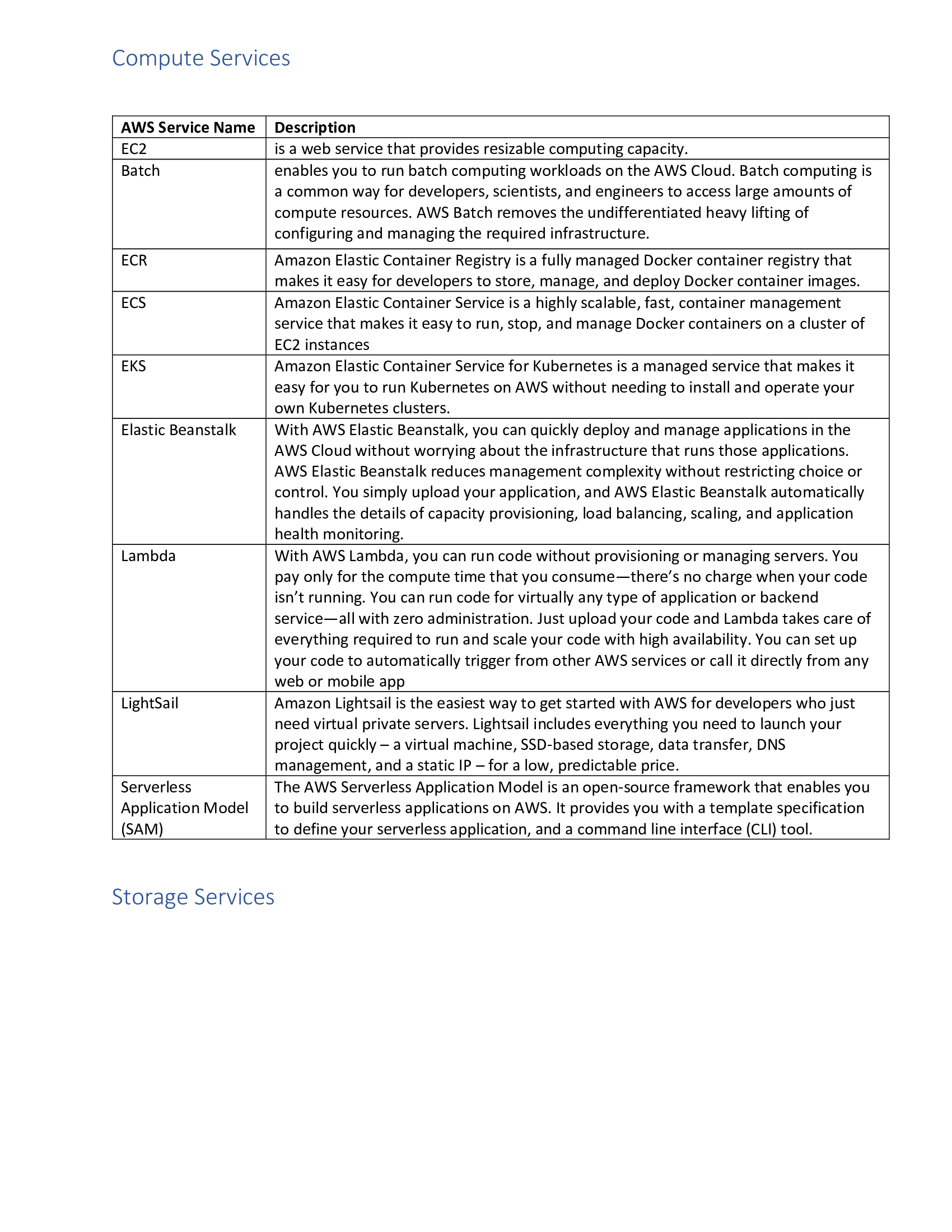
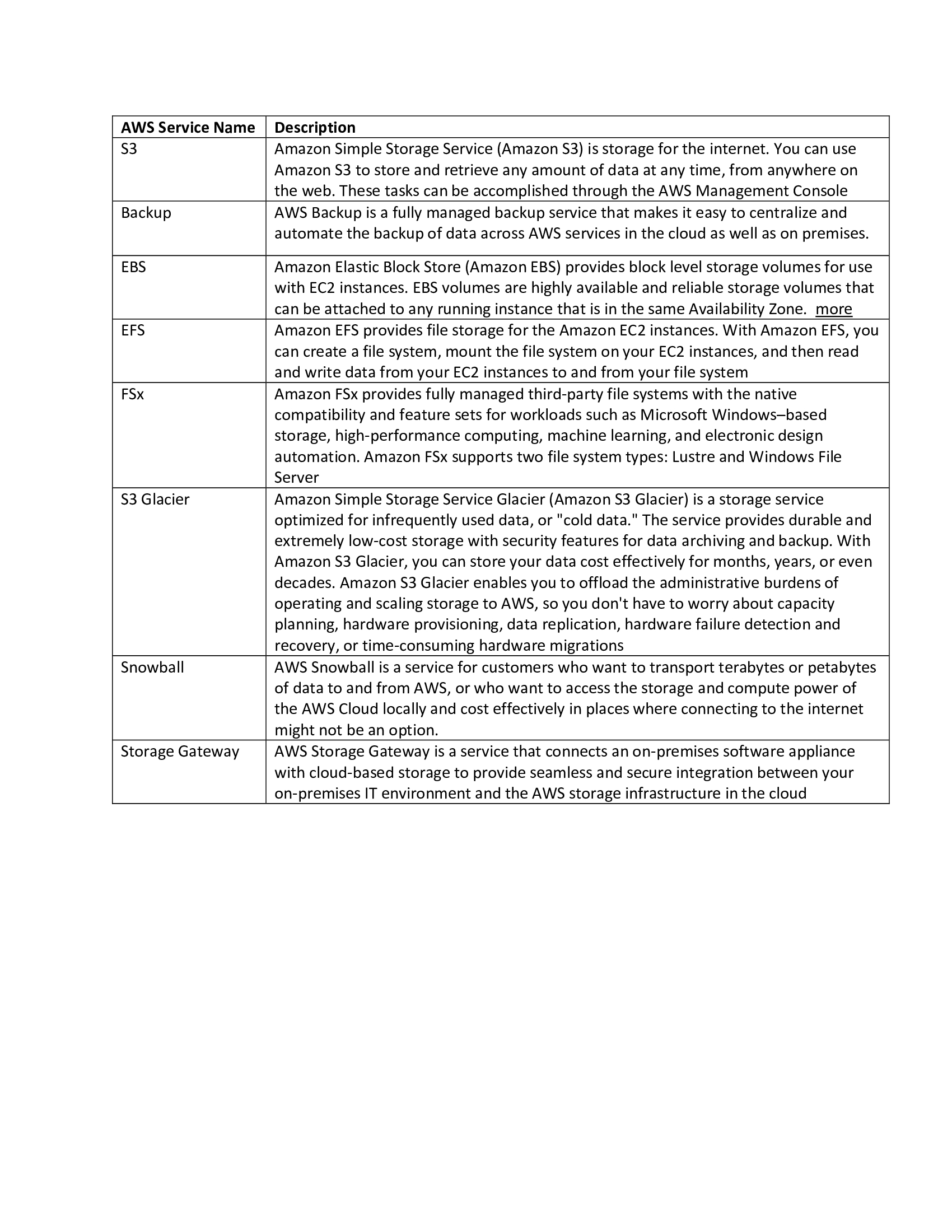
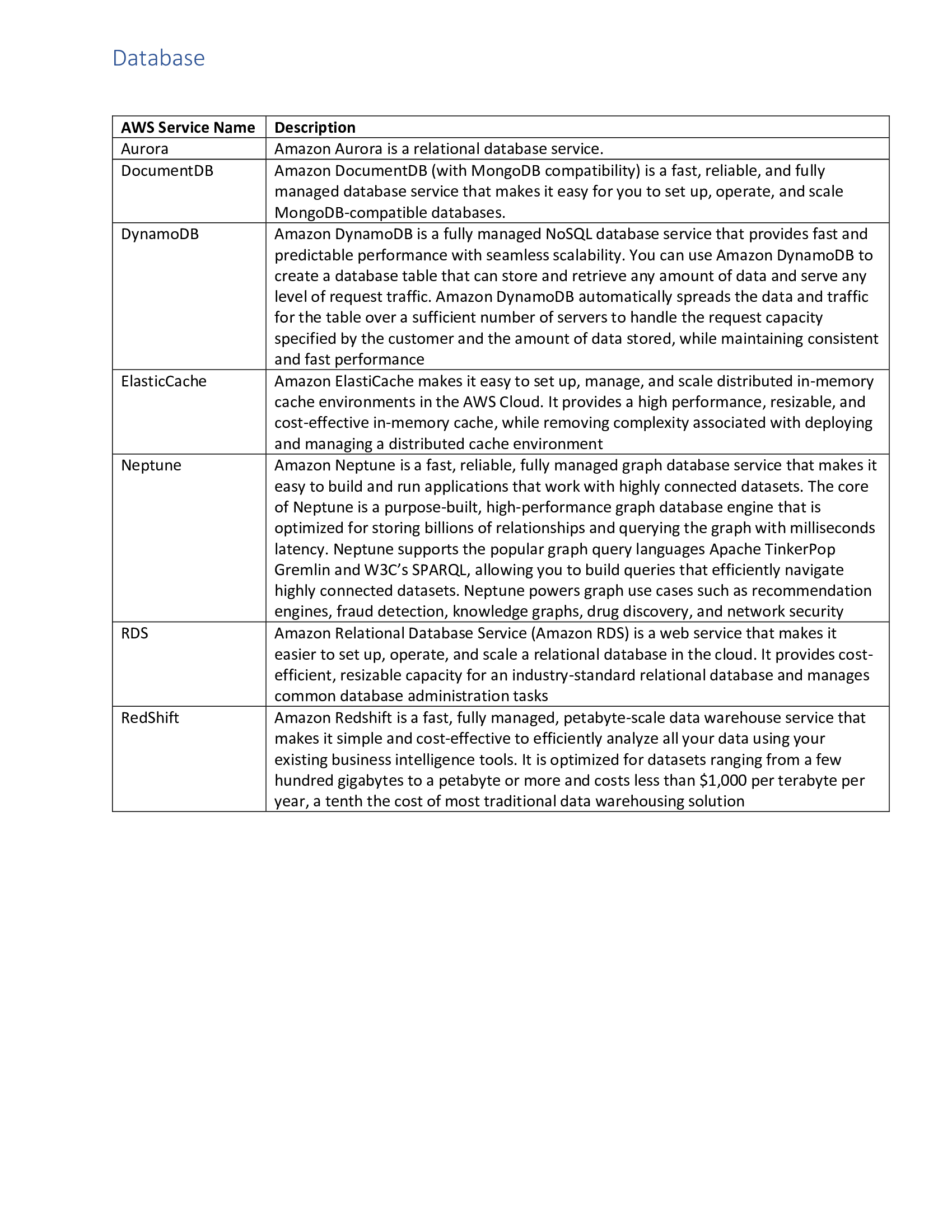
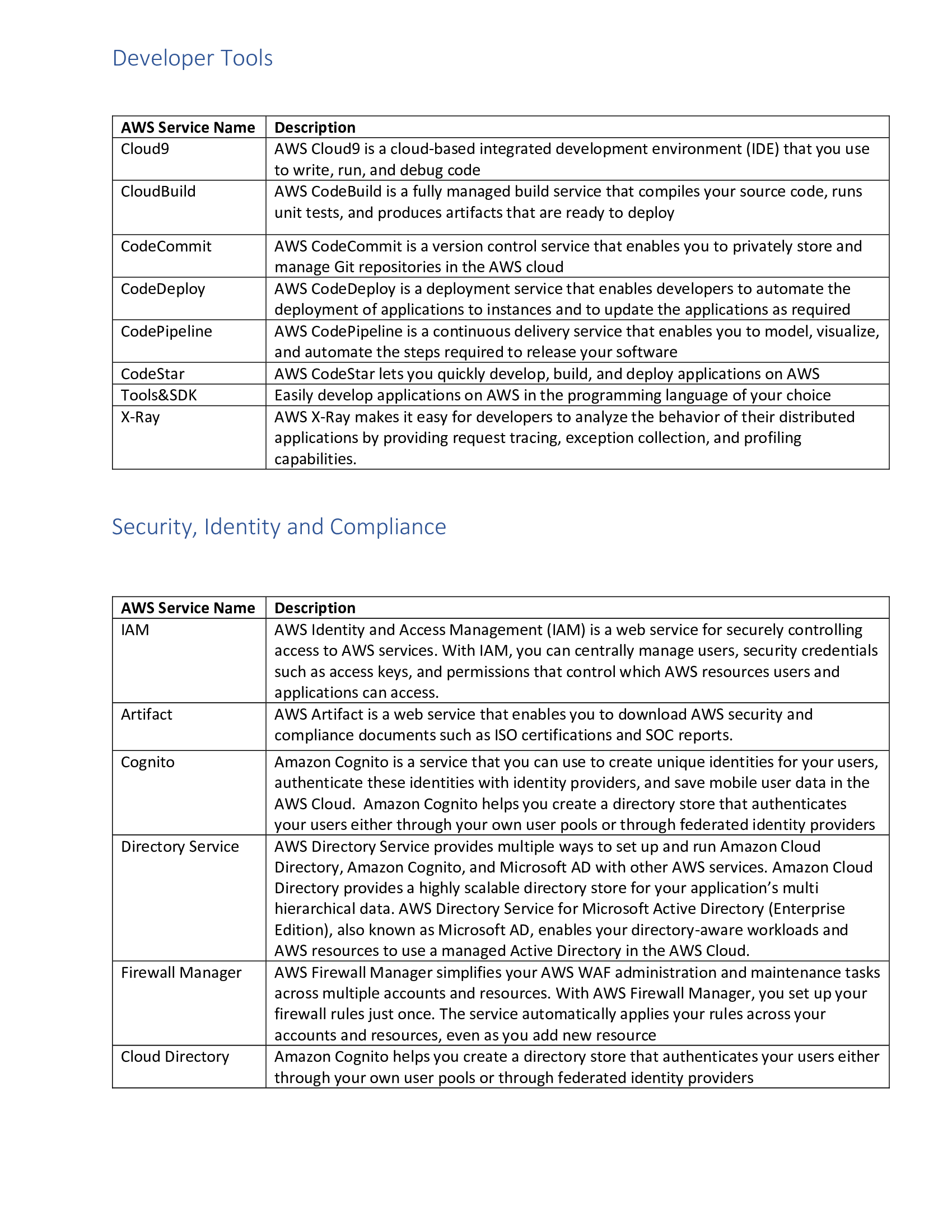
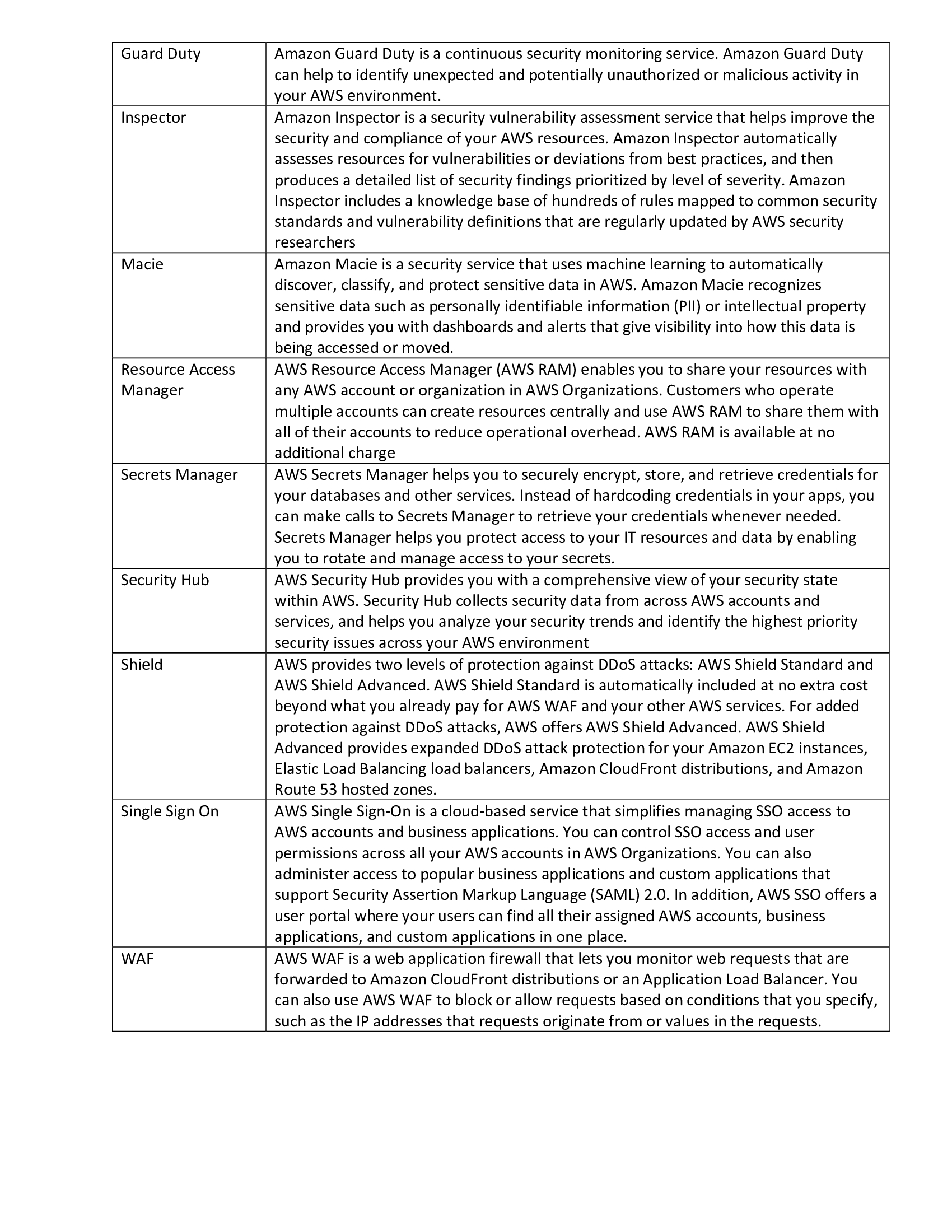
Ansible Service Names
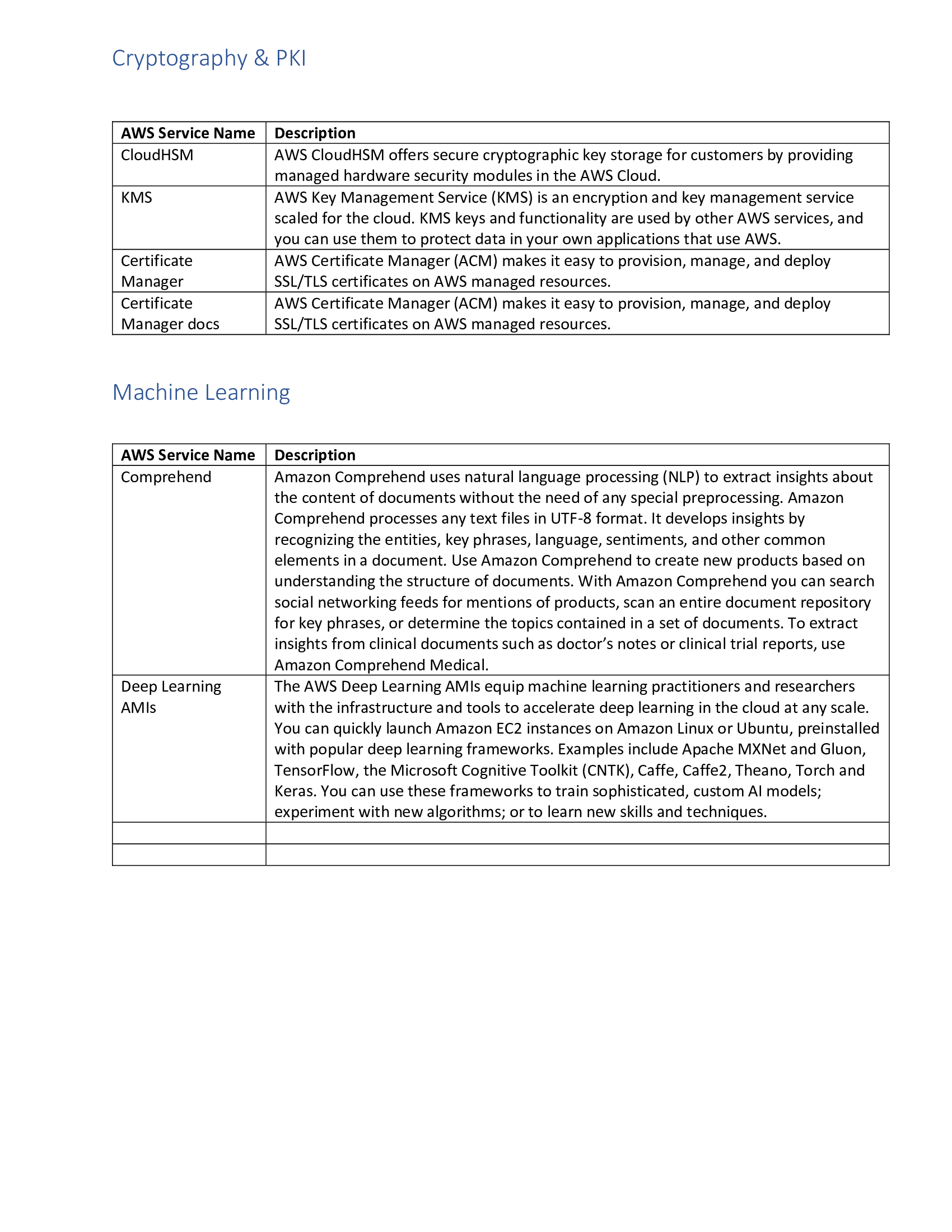

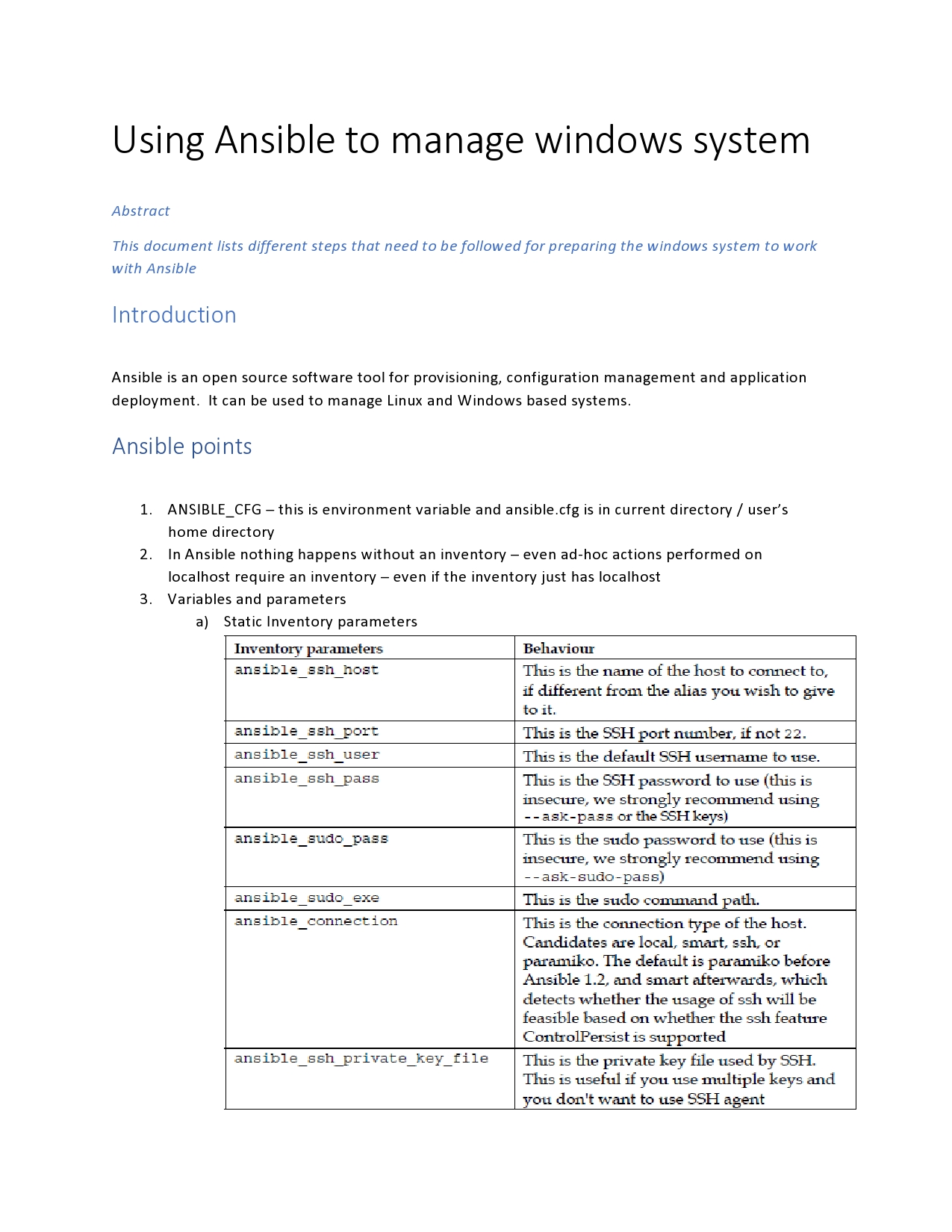
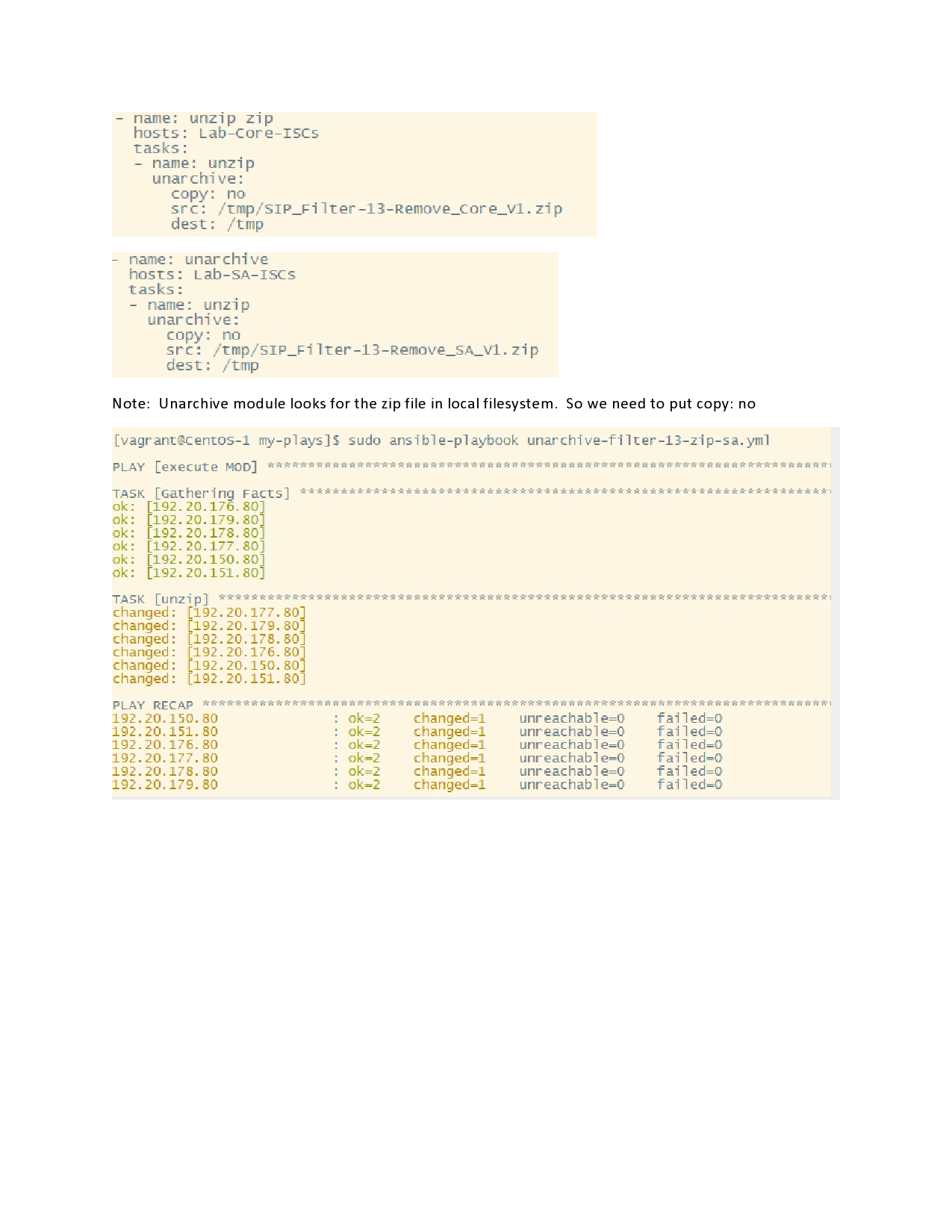
Using Ansible to manage Linux and Windows Systems
This topic describes what Ansible is, how to install it and how Ansible is used to manage Linux and Windows systems








Google Cloud Platform questions
This post lists useful topics and questions and their answers on GCP


12-factor process for app development
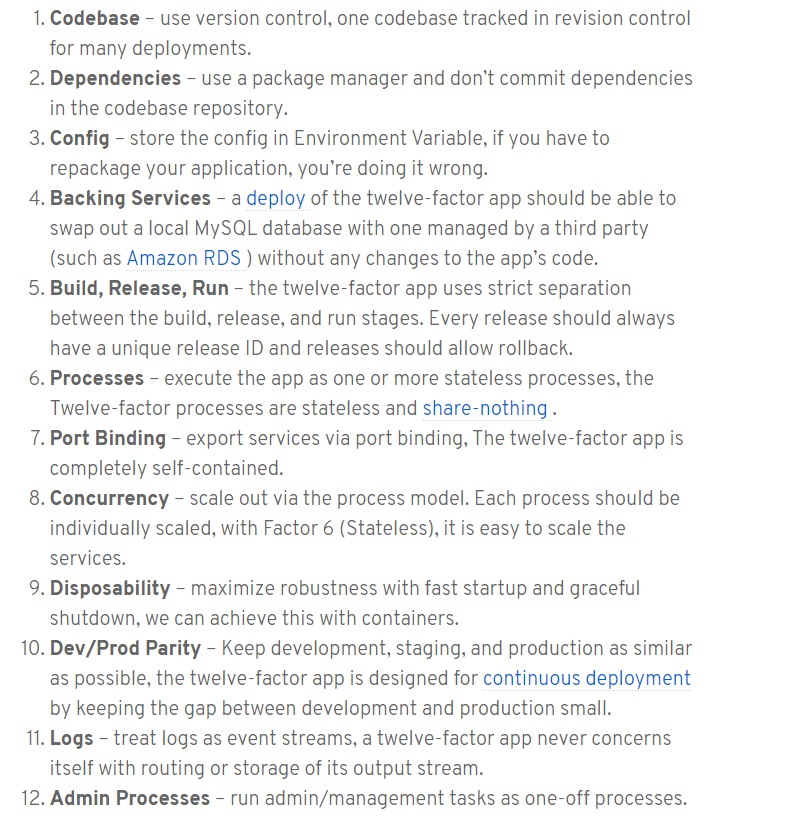


more will be added soon.
Windows Powershell commands
PowerShell is an interactive Command-Line Interface (CLI) and automation engine designed by Microsoft to help design system configurations and automate administrative tasks
- Get-Help : use this command to get help with any other command. E.g. to know how the Get-Process command works, type: Get-Help -Name Get-Process
- To get help using wildcard – Get-Help – Name Get-*
- Set-Execution-Policy: Microsoft has by default disabled scripting by default in an effort to prevent malicious code from executing in a PowerShell environment. So Set-Execution-Policy command to control the level of security surrounding PowerShell scripts. 4 levels of security are possible
- Restricted – restricted is the default execution policy and locks PowerShell down so that commands can be entered only interactively. PowerShell commands are not allowed to run
- All Signed – Here the scripts will be allowed to run, but only if they are signed by a trusted publisher
- Remote Signed – Here any locally created scripts and the remote ones only if they are signed by a trusted partner
- Unrestricted – no restrictions and all scripts can run.
- Get-Execution-Policy : get the current execution policy
- Get-Service: provides a list of all the services that are installed on the system. For a specific service, append the – Name switch and the name of the service (can use wildcards)
- ConvertTo-HTML : create a report to send to someone
- Export-CSV: Export data from PowerShell into a CSV file to open with Excel
- Select-Object: Allows to specify specific properties for inclusion. E.g. create a CSV file and use the command – Select-Object with Name to select certain properties
- GET-EventLog:
- Get-Process: similar to Get-Service command
- Stop-Process: to stop a particular process
more to come – executing PowerShell commands through Ansible.
About Myself
I am Ranjit with 20+ years experience in telecom, networking, cloud and virtualization technologies.
my linked in profile – https://www.linkedin.com/in/ranjitkav/
my email: ranjitkav@yahoo.com